
Subject expert Antoine Botte, co-founder and CTO of the Nucleon EDR cybersecurity solution and member of the OVHcloud tech ecosystem, talks to us about it today.
Why use artificial intelligence against cyber threats?
When it comes to cyber activities, which require a rapid response in cybersecurity, traditional malware detection methods such as signatures, sandboxing and heuristics have shown their limits.
These approaches, though widely used in the past, have proven to be resource-intensive and unable to keep pace with the ever-evolving pace of digital threats. Witnessing this boom, the Threat Intelligence Platform AV-ATLAS website is recording an uninterrupted flow of new strains of malware in real time.
With the exponential growth in the number of malware variants reported daily, the need for more sophisticated and responsive detection solutions is becoming crucial. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) takes a leading role.
Key areas to apply artificial intelligence in cybersecurity
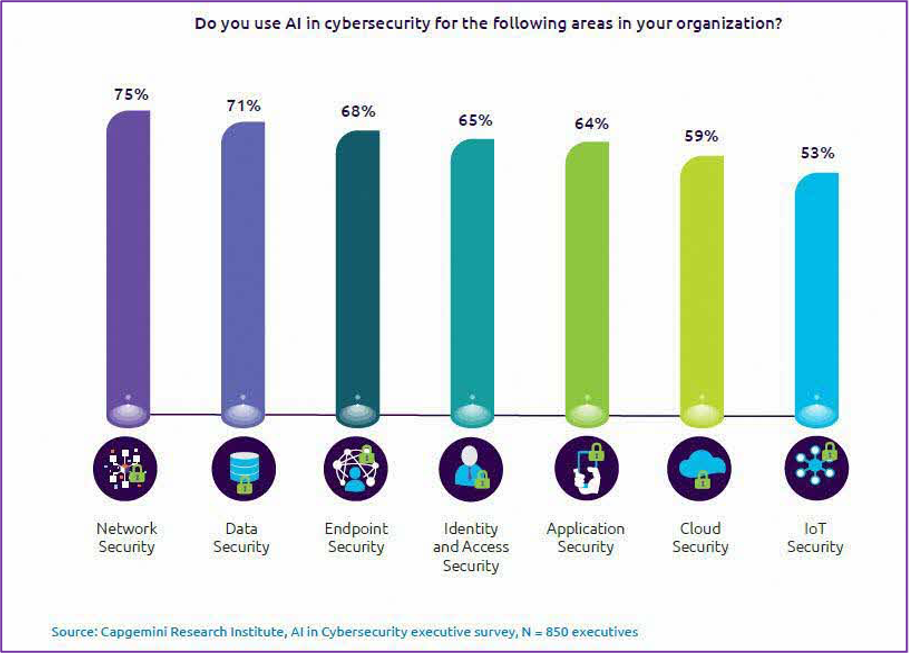
1 – Data analytics
One of the main contributions of AI to the security of digital devices and terminals is in advanced data analytics. Thanks to AI, in-depth analyses of security data is made possible, allowing trends and anomalies to be identified that could easily escape manual detection. This capability enables organisations to make informed security decisions based on accurate, real-time information, enhancing their ability to respond appropriately to threats and changing cybersecurity landscapes.
2 – Proactive prevention
Proactive prevention is another area where artificial intelligence shines. With AI technology, it is now possible to anticipate threats by identifying vulnerabilities before they are exploited. This predictive capability allows businesses to implement preventative measures, enhancing their data and systems protection before threats can cause damage. This proactive approach marks a significant step forward in securing digital infrastructures.
3 – Behavioural analysis
This uses AI as an effective way to prevent threats at an early stage. It allows for continuous monitoring by establishing a ‘normal’ behaviour model based on historical activity. It then scans the network for any elements that deviate from this standard at any given time. This analysis takes into account a variety of variables, including, but not limited to, the time and location of user connection attempts and the types of devices used. By referring to a predefined set of parameters, AI is able to quickly detect anomalies and instantly neutralise them. This approach is becoming increasingly accessible to organisations of all sizes, including through solutions such as those offered by Nucleon Security.
4 – Indicators of attack (IOA)
While AI-based cybersecurity currently focuses on indicators of compromise (IOC) to notify an organisation when a breach has occurred, AI can also provide indicators of attack (IOAs). Fundamentally, IOAs identify an attacker’s intent by looking at their objectives.
Indicators of attack use a combination of human skills and cloud-based machine learning to generate detailed data about an attacker’s behaviours. These IOAs can be used to build a precise picture of malicious behaviour and specific intentions.
Limitations and constraints related to the use of AI

However, artificial intelligence has some limitations.
1 – Detection rate
The detection rate for malicious behaviour or data at risk is not always 100%. While Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) software publishers frequently achieve detection rates above 99%, this may seem insufficient when you consider that over 2 million pieces of malware spread every week. There will always be threats that will escape detection.
2 – Lack of context
A key limitation of AI is its lack of contextual knowledge. In other words, AI does not take into account a company’s unique security policies or the specific purposes of the machines it protects. For example, the use of Dropbox can be harmless to some businesses while being strictly forbidden in others. Similarly, torrent download software can pose a threat by opening the door to unwanted programs, but its status varies depending on each organisation’s unique security needs and policies. This limitation highlights the importance of the human factor in contextualised security decision-making.
3 – Legal standards
Cybersecurity regulations may not always take the use of AI fully into account. This can create complications, particularly in terms of data management and privacy, defining legal responsibility, and the traceability and transparency of learning models.
Indeed, the use of AI in cybersecurity often involves the collection, analysis, and storage of sensitive data. Data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, impose strict requirements on how data should be handled. Businesses need to ensure that their AI practices comply with these regulations.
Furthermore, in the event of a security breach or AI incident, the question of legal liability may arise. Regulations have not always been clear on who is responsible for AI failure, which can lead to legal disputes.
Finally, regulations in some industries, such as finance and health, require that the decisions made by AI systems be explainable. Artificial intelligence, particularly the deep learning stage, can make it difficult, if not impossible, to explain the reasoning behind a decision, which can conflict with these transparency requirements.
Zero Trust model: keeping humans at the center
Human-related challenges remain an essential component of cybersecurity, even with artificial intelligence as an ally. While AI is a valuable asset, it is not self-sufficient. Security experts are still essential for interpreting the results produced by AI, making informed, contextual decisions, and refining security policies based on the specifics of each company. Human expertise remains crucial to ensuring effective protection against digital threats, even in an AI-powered environment.
To meet these challenges, the most effective solution is to adopt the Zero Trust model. This approach involves not trusting any program initially, tightly controlling its activities, and blocking any unknown elements. AI can be a powerful ally in this approach, but it cannot operate independently or in isolation.
AI must be embedded within a broader policy framework, which includes the active involvement of security specialists and constant vigilance to maintain the highest level of protection. This combination of technology and human surveillance is the most robust approach to addressing the complex challenges of modern cybersecurity.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is indeed a key driver for strengthening cybersecurity. However, its use must be carefully thought out, in harmony with strong security practices and a thorough understanding of each company’s unique needs and risks. By taking this balanced approach, we can prepare for the digital future with sound confidence, reaping the full benefits of AI while maintaining robust security tailored to the ongoing challenges of cybersecurity.
Nucleon Security offers advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions based on the Zero Trust paradigm coupled with artificial intelligence models, for a comprehensive protection approach. This detection and analysis approach is designed to anticipate and counter all threats, even the most modern and sophisticated.
The decision to host Nucleon Security solutions on OVHcloud infrastructures stems from a desire to guarantee optimal sovereignty and security. OVHcloud hosting services, as a leader in the field, offer a robust and reliable infrastructure that meets the highest data protection standards while retaining the flexibility we need to build our projects completely independently.
As a result, our solutions and products are available on the OVHcloud Marketplace, providing easy and secure access to our cutting-edge cybersecurity tools:
Nucleon EDR provides real-time monitoring, advanced behavioural analysis and proactive incident response. By combining these capabilities with the Zero Trust paradigm, Nucleon EDR ensures optimal security for your sensitive data, preventing attacks at an early stage.
Nucleon Cyclon Shield MDR is a comprehensive solution that helps to anticipate attacks, detect intrusions, and neutralise threats with unparalleled accuracy thanks to:
- Targeted threat anticipation through continuous business intelligence and a dedicated team of experts
- Sophisticated attack detection through in-depth analyses of suspicious events and behaviours, identification of weak signals, and use of indicators of compromise (IOC)
- Tailored responses based on personalised investigations, taking into account each customer’s context to understand the attackers’ tactics and providing precise, targeted recommendations.
Nucleon Malprob is a malware detection tool that uses advanced AI developed by our R&D teams. It’s a fully automated solution, offering the fastest analysis times on the market and real-time threat detection, for optimal security for your business. Nucleon Malprob can be easily integrated via application programming interfaces (APIs), making integration with existing systems simple and efficient.
